A brushed DC motor is a common type of motor that runs on direct current (DC) power. They are used in a variety of applications, from small consumer electronics to large industrial machinery. In this short introductory article, we'll take a closer look at how brushed DC motors work, their components, and their applications.
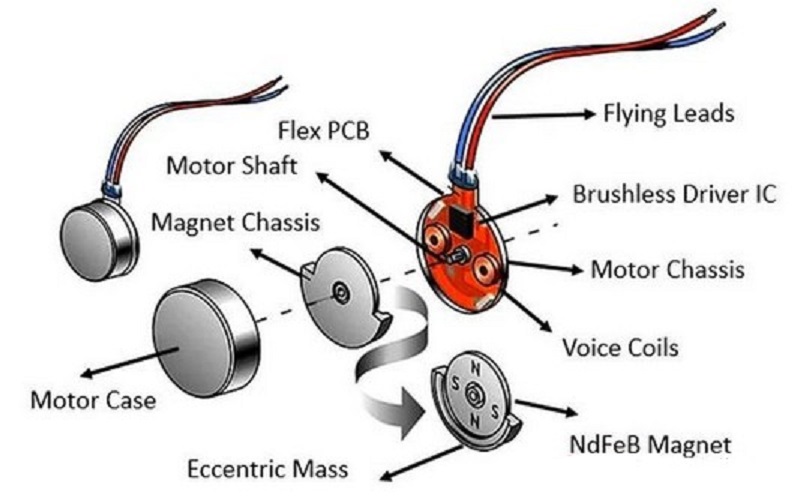
The basic operation of a 8mm diameter haptic motor involves the interaction of a magnetic field and electric current to produce motion. The main components of a brushed DC motor include the stator, rotor, commutator and brushes. The stator is the fixed part of the motor and contains the magnets or electromagnetic coils inside it, while the rotor is the rotating part of the motor and contains the armature. The commutator is a rotary switch that controls the flow of current to the armature, and brushes contact the commutator to transfer power to the armature.
When current is applied to a motor, a magnetic field is created in the stator. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor's magnetic field, causing the rotor to rotate. When the rotor rotates, the commutator and brushes work together to continuously switch the direction of the current flowing through the armature to ensure that the rotor continues to rotate in the same direction.
Working Principle
The operation of a brushed DC motor is rooted in the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction and the interaction between magnetic fields. When an electric current is supplied to the motor, the stator—whether equipped with permanent magnets or electromagnetic coils—generates a stable magnetic field. Simultaneously, the current flows through the armature windings on the rotor, transforming the rotor into an electromagnet. The magnetic field of the stator and the magnetic field of the rotor interact with each other, producing a rotational torque (Lorentz force) that causes the rotor to spin.
A critical aspect of sustaining continuous rotation in the same direction is the collaboration between the commutator and brushes. As the rotor turns, the commutator— a split-ring component attached to the rotor shaft—rotates in tandem. The brushes, typically made of carbon or graphite, maintain constant contact with the commutator segments. As the rotor reaches specific positions, the commutator switches the direction of the current flowing through the armature windings. This timely reversal of current ensures that the magnetic polarity of the rotor relative to the stator remains consistent, generating a continuous rotational force and preventing the rotor from stalling or reversing direction.
Performance Characteristics
Efficiency
The efficiency of brushed DC motors varies depending on their design, size, and operating conditions. Smaller brushed DC motors, such as those used in consumer electronics, typically have an efficiency range of 50-70%, while larger industrial-grade motors can achieve efficiencies of up to 85% or higher. The main factors affecting efficiency include brush-commutator friction, copper losses in the armature windings, iron losses in the stator and rotor cores, and mechanical losses (e.g., bearing friction). Brush wear and commutator degradation over time can also lead to a gradual decrease in efficiency.
Durability and Lifespan
The lifespan of a brushed DC motor is largely determined by brush and commutator wear. Under normal operating conditions, the brushes can last anywhere from a few thousand to tens of thousands of hours, depending on factors such as operating speed, load, temperature, and the quality of the brush and commutator materials. In high-speed or high-load applications, brush wear is accelerated, reducing the motor's lifespan. Additionally, the friction between the brushes and commutator generates dust and heat, which can further affect the motor's performance and durability if not properly managed.
Applications
While the original primer listed some key applications, brushed DC motors are used in a much wider range of scenarios due to their unique characteristics.
Consumer Electronics
Brushed DC motors are ubiquitous in consumer electronics, where their small size, low cost, and simple design make them ideal:
Portable devices: Vibrator motors in smartphones and tablets for haptic feedback (e.g., notifications, game controllers).
Home appliances: Motors in electric shavers, hair dryers, blenders, and vacuum cleaners.
Audio equipment: Turntable motors and cassette player motors (in vintage and some modern audio devices).
Robotics and Aerospace
Brushed DC motors are widely used in robotics and aerospace due to their compact size and high starting torque:
Small robots: Toy robots, educational robots, and hobbyist robots that require basic movement.
Medical Devices
In medical equipment, brushed DC motors are used in applications that require precise and reliable movement:
Wheelchairs: To provide mobility for individuals with disabilities, with speed control tailored to the user's needs.
Medical pumps: Infusion pumps and peristaltic pumps that deliver medications or fluids at a controlled rate.
Diagnostic equipment: Small motors in ultrasound machines and blood pressure monitors for mechanical movement.
Conclusion
In addition to their simple design and high starting torque, brushed DC motors are cost-effective and easy to use, making them a popular choice for many applications. However, they do have some limitations, such as limited speed control and higher maintenance requirements due to brush and commutator wear.
Despite these limitations, brushed DC motors are still widely used in various industries, including automotive, robotics, and aerospace. They are used in applications such as automotive power windows, windshield wipers and power seat adjustments, as well as robotic arms and actuators in industrial automation.
In summary, brushed DC motors are a versatile and reliable choice for many applications due to their simple design, high starting torque, and easy speed control. While they do have some limitations, their cost-effectiveness and availability make them a popular choice for a variety of industrial and consumer applications. As technology continues to advance, brushed DC coin motors are likely to continue to be an important part of the motor landscape in the coming years.
Consult Your Leader Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your micro brushless motor need, on-time and on budget.
Post time: Dec-16-2023