What Is Haptic / Tactile Feedback?
Haptic, or tactile, feedback is a technology that provides users with physical sensations in response to their movements or interactions with a device. It is commonly used in devices such as smartphones, game controllers, and wearables to enhance user experience. Tactile feedback can take various forms, such as vibrations, pulses, or motion. It aims to provide users with a more immersive and engaging experience by adding tactile elements to interactions with digital devices. For example, when you receive a notification on your smartphone, it may vibrate to provide tactile feedback. In video games, haptic feedback can simulate the feeling of an explosion or impact, making the gaming experience more realistic.
Notably, haptic/tactile feedback (often simply called "haptics") derives its name from the Greek phrase "I touch". It utilizes advanced vibration patterns and waveforms to convey information to users, differing from traditional audible and visual alerts like LEDs, beeps, and bells. While many products still rely on those old notification methods effectively in some scenarios, haptic feedback is in increasing demand to augment or replace them, especially as touch displays and interfaces become more prevalent in everyday products—these interfaces are cheaper to construct than control panels with buttons or switches, and designers can create context-specific user interfaces by simply adjusting the graphical layout on the screen.
It's also important to distinguish between haptic feedback and vibration alerting, as this is a common area of confusion with no strict guidelines. At its core, both use vibrations to interact with users, but the key difference lies in the complexity of the vibration pattern. Vibration alerting products are less complex, typically designed to produce a strong enough vibration to notify users of an event (e.g., a reversing car's parking sensor that makes the steering wheel vibrate when within 50 cm of an object). In contrast, haptic feedback devices use a variety of advanced waveforms to convey detailed information—for the parking sensor example, haptic feedback could vary the vibration strength or frequency based on the distance to the object, eliminating the high-pitched beeping of current sensors and ensuring usability even in loud environments or for those hard of hearing. Haptic feedback can also simulate clicks and button presses with predefined haptic waveforms, further enhancing the interactive experience.
Overall, haptic feedback is a technology designed to enhance user experience by adding a physical dimension to digital interactions, going beyond simple vibration alerts to deliver more nuanced and information-rich tactile responses.
How Does Haptic Feedback Work?
Haptic feedback works through the use of actuators, which are small devices that produce physical movement or vibration. These actuators are often embedded within the device and strategically placed to provide localized or widespread haptic effects. Haptic feedback systems use different types of actuators, including:
Eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors: These motors utilize an unbalanced mass on a rotating shaft to create vibrations as the motor rotates.
Linear Resonant Actuator (LRA): An LRA uses a mass attached to a spring to move back and forth quickly to create vibrations. These actuators can control amplitude and frequency more precisely than ERM motors.
Haptic feedback is triggered when a user interacts with the device, such as tapping a touch screen or pressing a button. The device's software or operating system sends signals to the actuators, instructing them to produce specific vibrations or movements. For example, if you receive a text message, your smartphone's software sends a signal to the actuator, which then vibrates to notify you. Tactile feedback can also be more advanced and sophisticated, with actuators capable of producing a variety of sensations, such as vibrations of varying intensities or even simulated textures.
Overall, haptic feedback relies on actuators and software instructions to provide physical sensations, making digital interactions more immersive and engaging for users.

Haptic Feedback Benefits (Used Small Vibration Motor)
Immersion:
Haptic feedback enhances the overall user experience by providing a more immersive interactive interface. It adds a physical dimension to digital interactions, allowing users to feel the content and engage with it. This is particularly beneficial in gaming and virtual reality (VR) applications, where haptic feedback can simulate touch, creating a deeper sense of immersion. For example, in VR games, haptic feedback can provide realistic feedback when users interact with virtual objects, such as feeling the impact of a fist or the texture of a surface.
Enhance Communication:
Haptic feedback enables devices to communicate information through touch, making it a valuable tool for user accessibility. For people with visual impairments, tactile feedback can serve as an alternative or complementary form of communication, providing tactile cues and feedback. For example, in mobile devices, haptic feedback can help visually impaired users navigate menus and interfaces by providing vibrations to indicate specific actions or options.
Improve Usability And Efficiency:
Haptic feedback helps improve usability and efficiency in a variety of applications. For example, in touchscreen devices, tactile feedback can provide confirmation of a button press or help the user locate a specific touch point, thereby reducing the possibility of mistaken or accidental touches. This makes the device more user-friendly and intuitive, especially for people with motor impairments or hand tremors.
Haptic Application
Gaming and Virtual Reality (VR): Haptic feedback is widely used in gaming and VR applications to enhance the immersive experience. It adds a physical dimension to digital interfaces, allowing users to feel and interact with virtual environments. Haptic feedback can simulate various sensations, such as the impact of a punch or the texture of a surface, making gaming or VR experiences more realistic and engaging.

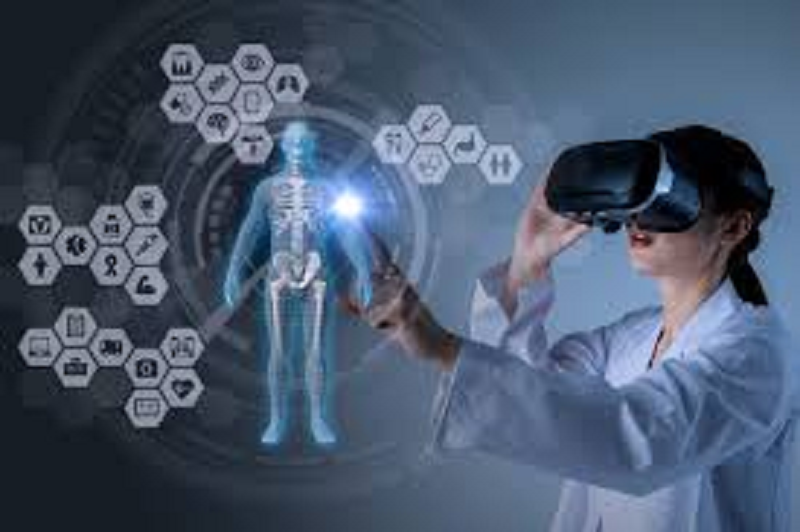
Medical training and simulation: Haptic technology has important uses in medical training and simulation. It enables medical professionals, students and trainees to practice various procedures and surgeries in a virtual environment, providing realistic touch feedback for accurate simulations. This helps healthcare professionals prepare for real-life scenarios, improve their skills, and enhance patient safety.

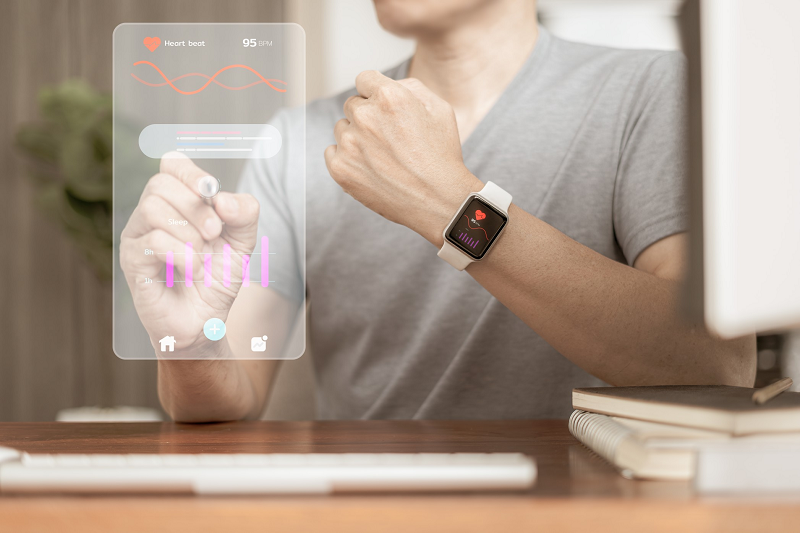
Wearable devices: Such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and augmented reality glasses use haptic technology to provide users with a sense of touch. Haptic feedback has multiple uses in wearable devices. First, it provides users with discreet notifications and alerts via vibration, allowing them to stay connected and informed without the need for visual or auditory cues. For example, a smartwatch can provide a slight vibration to notify the wearer of an incoming call or message. Second, tactile feedback can enhance interactions in wearable devices by providing tactile cues and responses. This is especially useful for touch-sensitive wearables, such as smart gloves or gesture-based controllers. Tactile feedback can simulate the feeling of touch or provide confirmation of user input, providing the wearer with a more intuitive and immersive interactive experience. Our linear resonant actuators (LRA Motor) are suitable for wearable devices.

Experience Haptic Feedback
Experiencing basic haptic feedback is fairly easy, as it is present in a variety of real-world applications and products—most people are familiar with simple haptics from using their smartphones, though this only scratches the surface of the technology's capabilities. If you’re interested in experimenting with advanced haptic feedback but don’t want to build detailed circuitry, exploring haptic feedback evaluation kits is a perfect solution. Such kits typically simulate both handheld products and mounted capacitive touch surfaces in one setup, allowing you to evaluate haptic feedback effects and easily share findings with colleagues or teams. They serve as an easy first step to understanding how to improve products with haptics. Alternatively, if you’re ready to build your own haptic feedback system or want more in-depth technical details, resources on circuit design and implementation (such as guides on "Adding and Improving Haptic Feedback") can provide the necessary information to create an effective haptic feedback solution.
Consult Your Leader Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your micro brushless motor need, on-time and on budget.
Post time: Dec-01-2023